The Logstash Elasticsearch plugins (output,input,filterand monitoring)support authentication and encryption over HTTP.
To use Logstash with a secured cluster, you need to configure authenticationcredentials for Logstash. Logstash throws an exception and the processingpipeline is halted if authentication fails.
If encryption is enabled on the cluster, you also need to enable TLS/SSL in theLogstash configuration.
If you want to monitor your Logstash instance with X-Pack monitoring, and store themonitoring data in a secured Elasticsearch cluster, you must configure Logstashwith a username and password for a user with the appropriate permissions.
In addition to configuring authentication credentials for Logstash, you needto grant authorized users permission to access the Logstash indices.
Configuring Logstash to use Basic Authentication
Logstash needs to be able to manage index templates, create indices,and write and delete documents in the indices it creates.
To set up authentication credentials for Logstash:
Use the the Management > Roles UI in Kibana or the
roleAPI to create alogstash_writerrole. For cluster privileges, addmanage_index_templatesandmonitor.For indices privileges, addwrite,delete, andcreate_index.If you plan to use index lifecyclemanagement, also add
manage_ilmfor cluster andmanageandmanage_ilmfor indices.POST _xpack/security/role/logstash_writer{ "cluster": ["manage_index_templates", "monitor", "manage_ilm"],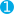 "indices": [ { "names": [ "logstash-*" ],
"indices": [ { "names": [ "logstash-*" ],  "privileges": ["write","delete","create_index","manage","manage_ilm"]
"privileges": ["write","delete","create_index","manage","manage_ilm"]  } ]}
} ]}The cluster needs the
manage_ilmprivilege ifindex lifecycle managementis enabled.If you use a custom Logstash index pattern, specify your custom patterninstead of the default
logstash-*pattern.If index lifecyclemanagement is enabled, the role requires the
manageandmanage_ilmprivileges to load index lifecycle policies, create rollover aliases, and createand manage rollover indices.Create a
logstash_internaluser and assign it thelogstash_writerrole.You can create users from the Management > Users UI in Kibana or throughtheuserAPI:POST _xpack/security/user/logstash_internal{ "password" : "x-pack-test-password", "roles" : [ "logstash_writer"], "full_name" : "Internal Logstash User"}Configure Logstash to authenticate as the
logstash_internaluser you justcreated. You configure credentials separately for each of the Elasticsearch plugins inyour Logstash.conffile. For example:input { elasticsearch { ... user => logstash_internal password => x-pack-test-password }}filter { elasticsearch { ... user => logstash_internal password => x-pack-test-password }}output { elasticsearch { ... user => logstash_internal password => x-pack-test-password }}
Granting Users Access to the Logstash Indices
To access the indices Logstash creates, users need the read andview_index_metadata privileges:
Create a
logstash_readerrole that has thereadandview_index_metadataprivileges for the Logstash indices. You can create roles from theManagement > Roles UI in Kibana or through theroleAPI:Assign your Logstash users the
logstash_readerrole. If the Logstash userwill be usingcentralized pipeline management,also assign thelogstash_adminrole. You can create and manage users from theManagement > Users UI in Kibana or through theuserAPI:
Configuring the Elasticsearch Output to use PKI Authentication
The elasticsearch output supports PKI authentication. To use an X.509client-certificate for authentication, you configure the keystore andkeystore_password options in your Logstash .conf file:
output { elasticsearch { ... keystore => /path/to/keystore.jks keystore_password => realpassword truststore => /path/to/truststore.jks 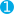 truststore_password => realpassword }}
truststore_password => realpassword }}
Configuring Logstash to use TLS Encryption
If TLS encryption is enabled on the Elasticsearch cluster, you need toconfigure the ssl and cacert options in your Logstash .conf file:
Configuring Credentials for Logstash Monitoring
If you plan to ship Logstash monitoringdata to a secure cluster, you need to configure the username and password thatLogstash uses to authenticate for shipping monitoring data.
X-Pack security comes preconfigured with alogstash_system built-in userfor this purpose. This user has the minimum permissions necessary for themonitoring function, and should not be used for any other purpose - it isspecifically not intended for use within a Logstash pipeline.
By default, the logstash_system user does not have a password. The user willnot be enabled until you set a password. Set the password through the changepassword API:
PUT _xpack/security/user/logstash_system/_password{ "password": "t0p.s3cr3t"}
Then configure the user and password in the logstash.yml configuration file:
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: logstash_systemxpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: t0p.s3cr3t
If you initially installed an older version of X-Pack, and then upgraded, thelogstash_system user may have defaulted to disabled for security reasons.You can enable the user through the user API:
PUT _xpack/security/user/logstash_system/_enable
Configuring Credentials for Centralized Pipeline Management
If you plan to use Logstashcentralized pipeline management,you need to configure the username and password that Logstash uses for managingconfigurations.
You configure the user and password in the logstash.yml configuration file: